Navigation auf uzh.ch
Navigation auf uzh.ch
Project aims
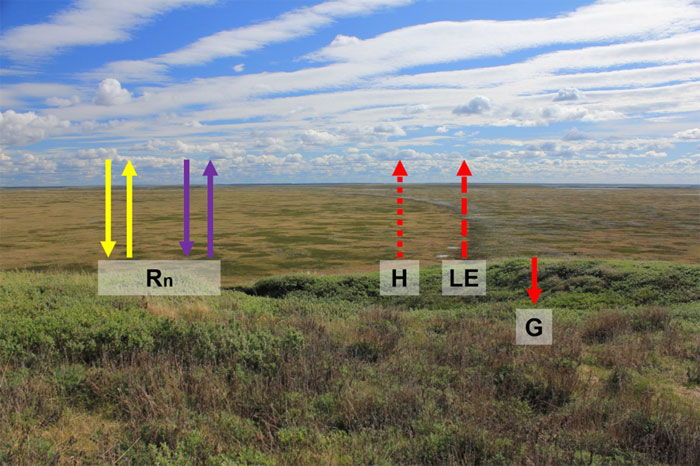
The Arctic is one of Earths’ regions most heavily influenced by climate change. A change in climate also reflects changes to surface energy fluxes, which play a pivotal role in Earth system dynamics (Fig. 1). We want to understand the role of energy fluxes in shaping interactions and feedbacks within the earth system (i.e. carbon cycle, water cycle, permafrost dynamics, biodiversity change, etc.) under current and future climate scenarios. We will address this goal by integrating knowledge from literature, using an experimental approach in the Arctic tundra (cf. TRAIN experiment; Figs. 2 and 3), and using the DART 3D radiative transfer model with in silico plant communities (Fig. 4).



Elena Plekhanova, Jacqueline Oehri, Raleigh Grysko, Gabriela Schaepman-Strub